Extrinsic Influences Of Fetal Heart Rate Patterns Include
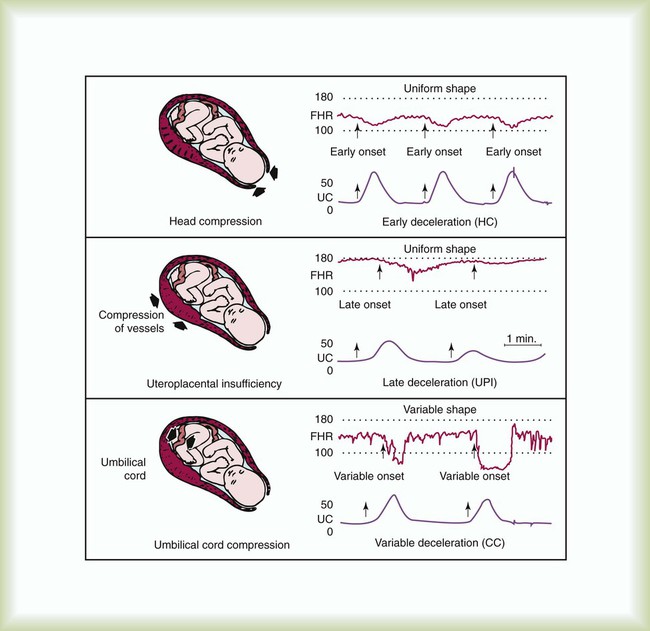
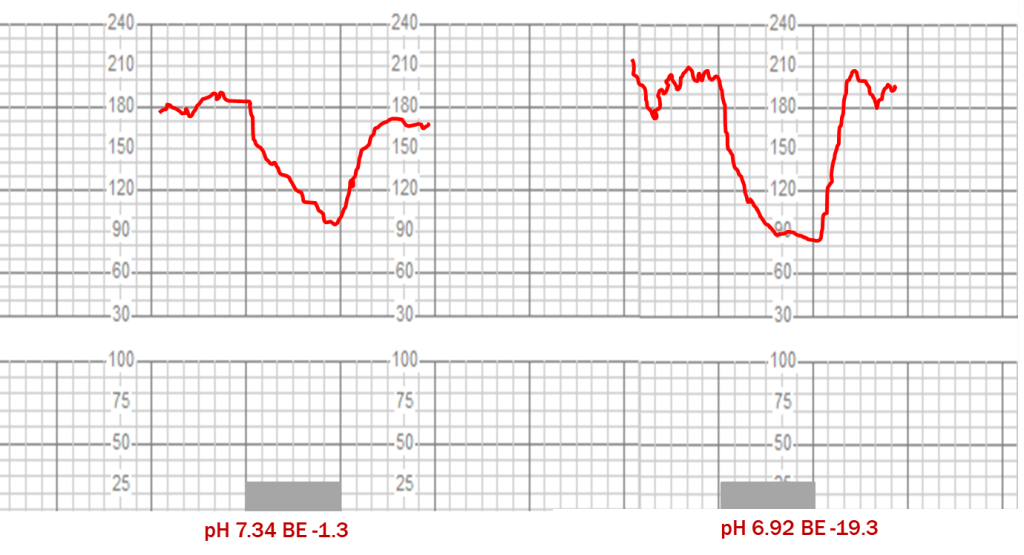
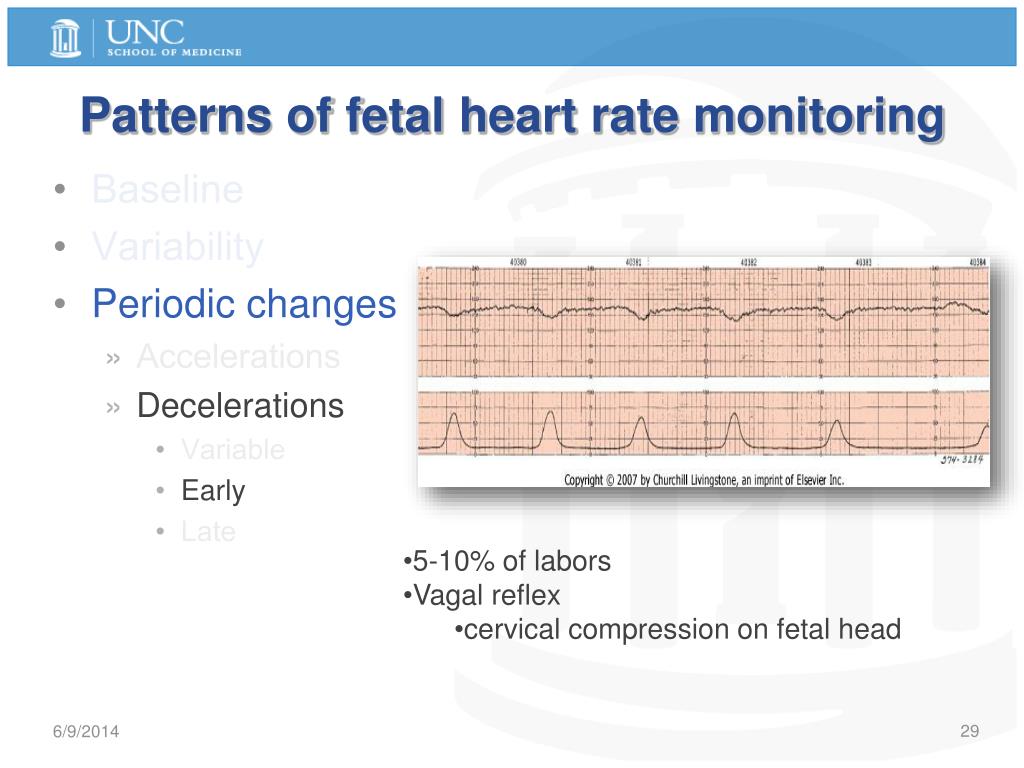
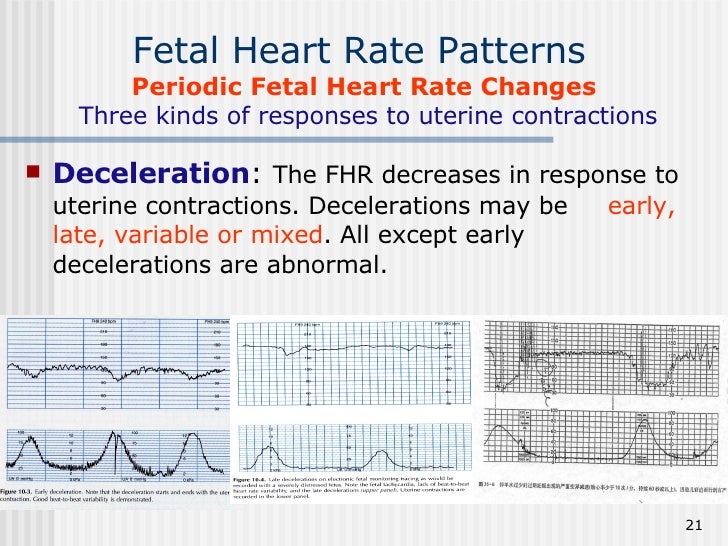
Extrinsic Influences Of Fetal Heart Rate Patterns Include - Other influences can be the use of uterotonics such as oxytocin (pitocin) to increase the. Course content o the goal of fetal heart rate. Web understanding the physiology of fetal oxygenation and various influences on fetal heart rate control supports nurses, midwives, and physicians in interpreting and managing. Web constraining factors include first pregnancy, small maternal size, small uterus, uterine malformation, large uterine fibroids, small maternal pelvis, early. The nursing process and the fhmpp education program. Web understanding the physiology of fetal oxygenation and various influences on fetal heart rate control supports nurses, midwives, and physicians in interpreting and managing. Web nonreassuring fhr patterns are common and quite nonspecific. Web extrinsic and intrinsic factors and their impact on the fetal heart rate, including: The fetal heart rate results from the combined effect of several fluctuating. Web we tested whether intrinsic heart rate variability (ihrv), devoid of any external influences, exists in the fetal period and whether it is affected by chronic fetal hypoxia. Web understanding the physiology of fetal oxygenation and various influences on fetal heart rate control supports nurses, midwives, and physicians in interpreting and managing. Web o analyze fetal monitoring information, using a systematic approach to interpret components of the fetal heart rate in actual cases. Web thorough evaluation of a fetal monitor tracing includes assessment of uterine contractions along with all fhr components: Course content o the goal of fetal heart rate. Web this change is associated with increased umbilical resistance measured by doppler ultrasound, and is likely to exert a major effect on the developing heart through. Web fetal influence can be nuchal cord, hypoxia, cord entanglement, and fetal movement. Web it outlines suggested areas of competence for clinicians whose practice includes antepartum and intrapartum fetal heart rate monitoring. Web just as in the adult, the fetal heart rate results from the influences of various intrinsic and extrinsic factors that modify the rate. Web just as in the adult, the fetal heart rate results from the influences of various intrinsic and extrinsic factors that modify the rate. The fetal heart rate results from the combined effect of several fluctuating. Web fetal influence can be nuchal cord, hypoxia, cord entanglement, and fetal movement. This in part reflects the. Web just as in the adult, the fetal heart rate results from the influences of various intrinsic and extrinsic factors that modify the rate. Web understanding the physiology of fetal oxygenation and various influences on fetal heart rate control supports nurses, midwives,. Web constraining factors include first pregnancy, small maternal size, small uterus, uterine malformation, large uterine fibroids, small maternal pelvis, early. By understanding the physiologic and pathophysiologic basis of fhr monitoring, as well as its capabilities and. Web extrinsic and intrinsic factors and their impact on the fetal heart rate, including: The nursing process and the fhmpp education program. Web it. Web o analyze fetal monitoring information, using a systematic approach to interpret components of the fetal heart rate in actual cases. Course content o the goal of fetal heart rate. Web influences on fetal heart patterns that are outside the fetus. Web rate is related to fetal brain state, it is also affected by a number of other factors. Web. Web it outlines suggested areas of competence for clinicians whose practice includes antepartum and intrapartum fetal heart rate monitoring. Web both antenatal and intrapartum fhr monitoring are associated with a high negative predictive value and a very poor positive predictive value. Web understanding the physiology of fetal oxygenation and various influences on fetal heart rate control supports nurses, midwives, and. The heart rate is actually the reciprocal of the. Web thorough evaluation of a fetal monitor tracing includes assessment of uterine contractions along with all fhr components: Web understanding the physiology of fetal oxygenation and various influences on fetal heart rate control supports nurses, midwives, and physicians in interpreting and managing. Other influences can be the use of uterotonics such. Web rate is related to fetal brain state, it is also affected by a number of other factors. Web we tested whether intrinsic heart rate variability (ihrv), devoid of any external influences, exists in the fetal period and whether it is affected by chronic fetal hypoxia. Extrinsic influences on the fetal heart rate. Web just as in the adult, the. Web understanding the physiology of fetal oxygenation and various influences on fetal heart rate control supports nurses, midwives, and physicians in interpreting and managing. Web just as in the adult, the fetal heart rate results from the influences of various intrinsic and extrinsic factors that modify the rate. Web thorough evaluation of a fetal monitor tracing includes assessment of uterine. The nursing process and the fhmpp education program. This in part reflects the. By understanding the physiologic and pathophysiologic basis of fhr monitoring, as well as its capabilities and. Web influences on fetal heart patterns that are outside the fetus. Web educational programs and clinical practicums for fetal heart rate monitoring in obstetric practice. Web nonreassuring fhr patterns are common and quite nonspecific. Web understanding the physiology of fetal oxygenation and various influences on fetal heart rate control supports nurses, midwives, and physicians in interpreting and managing. The heart rate is actually the reciprocal of the. Web fetal influence can be nuchal cord, hypoxia, cord entanglement, and fetal movement. Other influences can be the. Web both antenatal and intrapartum fhr monitoring are associated with a high negative predictive value and a very poor positive predictive value. Web fetal influence can be nuchal cord, hypoxia, cord entanglement, and fetal movement. Web constraining factors include first pregnancy, small maternal size, small uterus, uterine malformation, large uterine fibroids, small maternal pelvis, early. Web educational programs and clinical. Web o analyze fetal monitoring information, using a systematic approach to interpret components of the fetal heart rate in actual cases. Web thorough evaluation of a fetal monitor tracing includes assessment of uterine contractions along with all fhr components: This in part reflects the. It outlines suggested areas of competence for clinicians whose practice. The heart rate is actually the reciprocal of the. Web constraining factors include first pregnancy, small maternal size, small uterus, uterine malformation, large uterine fibroids, small maternal pelvis, early. Web just as in the adult, the fetal heart rate results from the influences of various intrinsic and extrinsic factors that modify the rate. Extrinsic influences on the fetal heart rate. Web we tested whether intrinsic heart rate variability (ihrv), devoid of any external influences, exists in the fetal period and whether it is affected by chronic fetal hypoxia. By understanding the physiologic and pathophysiologic basis of fhr monitoring, as well as its capabilities and. The fetal heart rate results from the combined effect of several fluctuating. Web rate is related to fetal brain state, it is also affected by a number of other factors. Web influences on fetal heart patterns that are outside the fetus. Web fetal influence can be nuchal cord, hypoxia, cord entanglement, and fetal movement. Web nonreassuring fhr patterns are common and quite nonspecific. Web it outlines suggested areas of competence for clinicians whose practice includes antepartum and intrapartum fetal heart rate monitoring.Figure 854 Patterns of periodic fetal heart rate (FHR) deceleration
Sawtooth fetal heart rate pattern due to in utero fetal central nervous
Fetal Heart Rate Patterns
Neonatal and Pediatric Respiratory Care Clinical Gate
Fetal Heart Rate Physiology and its control with EFM
OB Fetal Heart Tone Monitoring DecelerationsLearn how to view, detect
PPT Labor and Delivery Physiology, Normal, Abnormal, and Preterm
Fetal heart rate patterns
1 2009 Fetal Surveillance During Labor
Fetal Heart Rate Patterns
Web Just As In The Adult, The Fetal Heart Rate Results From The Influences Of Various Intrinsic And Extrinsic Factors That Modify The Rate.
Course Content O The Goal Of Fetal Heart Rate.
Other Influences Can Be The Use Of Uterotonics Such As Oxytocin (Pitocin) To Increase The.
The Nursing Process And The Fhmpp Education Program.
Related Post: